Customizing systemd services#
By default, TLJH configures two systemd services to run JupyterHub and Traefik.
These services come with a default set of settings, which are specified in jupyterhub.service and traefik.service. They look like the following:
[Unit]
Requires=traefik.service
After=traefik.service
[Service]
User=root
Restart=always
WorkingDirectory=/opt/tljh/state
PrivateTmp=yes
PrivateDevices=yes
ProtectKernelTunables=yes
ProtectKernelModules=yes
Environment=TLJH_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/tljh
ExecStart=/opt/tljh/hub/bin/python3 -m jupyterhub.app -f jupyterhub_config.py --upgrade-db
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
However in some cases, admins might want to have better control on these settings.
For example when mounting shared volumes over the network using Samba, these namespacing settings might be a bit too strict and prevent users from accessing the shared volumes.
Overriding settings with override.conf#
To override the jupyterhub settings, it is possible to provide a custom /etc/systemd/system/jupyterhub.service.d/override.conf file.
Here is an example for the content of the file:
[Service]
PrivateTmp=no
PrivateDevices=no
ProtectKernelTunables=no
ProtectKernelModules=no
This example should be useful in the case of mounting volumes using Samba and sharing them with the JupyterHub users. You might also want to provide your own options, which are listed in the systemd documentation.
Then make sure to reload the daemon and the jupyterhub service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart jupyterhub
Then check the status with:
sudo systemctl status jupyterhub
The output should look like the following:
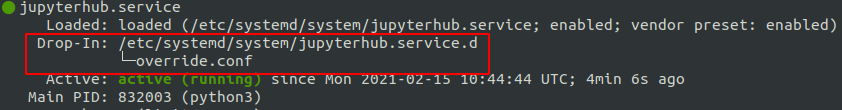
To override the traefik settings, create a new file under /etc/systemd/system/traefik.service.d/override.conf
and follow the same steps.
References#
If you would like to learn more about the systemd security features, check out these references:
